Routine Maintenance Extends Life of Semi-Hermetic Compressors
Do you live in an area that has experienced some of the sweltering heat waves that have plagued the United States the last several years? While scientists and politicians may squabble over the causes of and solutions to the record temperatures we’re seeing, it’s a simple fact that the last few years have been some of the hottest on record.
While increasing global temperatures present a whole host of problems, there’s one industry that’s staying busier than ever when the heat is on. That’s right. We’re talking about the heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration industry, more commonly referred to as HVACR.
HVACR professionals, from installers to technicians, keep the machines that make our lives comfortable and enjoyable running smoothly. From the central air conditioning unit that keeps your home cool to the industrial refrigeration units that chill your foods and beverages at the local grocery and convenience store, it’s hard to imagine modern life without the convenience of a wide variety of HVACR equipment.
Unfortunately, the HVACR industry is dealing with the same shortage of highly-skilled workers that manufacturing and dozens of other industries across the country have been facing for years. There simply aren’t enough qualified workers to fill the open positions available in the HVACR industry.
That’s why highly-skilled HVACR technicians are in such great demand these days. Today’s HVACR technicians need expertise with a wide variety of common HVACR components. For example, when dealing with large air conditioning systems or commercial refrigeration units, in-depth knowledge of and experience with compressors is essential.
Some of these systems may feature hermetic compressors, which seal both the motor and compressor inside a leak-proof welded steel shell. Unfortunately, this design makes basic repairs impossible. If the unit fails, it must simply be replaced.
That’s why the design of semi-hermetic compressors has become a popular choice for these systems today. Semi-hermetic compressors also protect the motor and compressor inside a sealed shell. However, unlike hermetic compressors, semi-hermetic compressors can be opened to provide access to many essential mechanical parts, so that they can be maintained and repaired rather than replaced.
Performing routine maintenance on semi-hermetic compressors can extend their service life by many years, saving thousands of dollars. With proper care and maintenance, semi-hermetic compressors can perform at peak efficiency for 8-10 years or more.
If you want to teach an aspiring HVACR technician how to maintain and repair a semi-hermetic compressor, DAC Worldwide’s Semi-Hermetic Compressor Cutaway (373-120) is an expertly-sectioned example of a common intermediate (1”-1 ½”) horsepower semi-hermetic refrigeration compressor that facilitates and supports practical training in compressor design, operating principles, and maintenance.
This unique training tool features a full longitudinal cutaway of a semi-hermetic compressor, which allows for full visibility of the compressor’s operating components, including multiple cylinders, valves, internal motor, and crank shaft. Multiple cutaways unveil all internal components, and cutaway surfaces are enhanced through painting, making the geometry of all components more clear.
The Semi-Hermetic Compressor Cutaway is only one of DAC Worldwide’s many HVACR training cutaways. Visit DAC Worldwide online to learn more about other HVACR training tools, such as the Hermetic Scroll Refrigeration Compressor Cutaway, the Open Drive Refrigeration Compressor Cutaway, the ACR Solenoid Valve Cutaway, and more!
- Published in News
DAC Worldwide’s Oil Cooler Cutaway Provides Unique Training Opportunity
Many manufacturing processes require the transfer of heat from one fluid (liquid or gas) to another, and most of those processes use heat exchangers to accomplish this task. In a heat exchanger, the two fluids do not make direct contact. Instead, heat passes from the hotter fluid to the metal isolating the fluids and then to the cooler fluid.
You’ll find heat exchangers in a wide variety of industrial applications, including heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems; preheaters or coolers in fluid systems; radiators on internal combustion engines; and boilers, evaporators, and condensers used with fluids like oils, wastewater, hydrocarbons, biogases, etc. in industries such as oil and gas refining and power generation.
Heat exchangers come in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and designs. For example, a finned tube oil cooler is a specific type of heat exchanger used to cool fluids, such as oil. A finned tube oil cooler features a bundle of tubes with fins that increase the surface area usable for heat transfer.
The tubes in a finned tube oil cooler can be made of a variety of materials, including aluminum, copper, or stainless steel. The fins are often made of the same material, although they can be made from another material, like carbon steel.
A finned tube oil cooler cools oil by circulating the oil through the tubes while water or another cooling fluid flows over the fins. The oil’s heat transfers from the fluid to the fins first and then to the cooling fluid, which transports the heat out of the system.
DAC Worldwide’s Oil Cooler Cutaway, Finned Tube Bundle-Type (273-610F) is a desktop training tool for industrial heat exchanger training that supports operations and skills training relating to this common device found in process systems of all types.
Finned tube heat exchangers have a wide variety of applications in the oil & gas, petrochemical, and power industries. These heat exchangers offer reliable operation, low operating costs, and high performance.
Oil coolers have some specific advantages. Oil has a higher boiling point than water, so it can be used to cool items 100°C or higher. In addition, oil is an electrical insulator, so it can be used inside of or in direct contact with electrical components.
Multiple cutaways unveil primary details and features, including tube layout, tube sheets, aluminum fins, nozzles, flow path, and gaskets. The cutaway consists of an actual industrial, 2-pass, heat exchanger/cooler. Common makes and models are chosen for industrial training relevance.
Mounted on a powder-coated, formed-steel mounting stand and allowing mounting on standard DAC Worldwide display and storage products, the device will provide years of use in any industrial training program.
DAC Worldwide’s Oil Cooler Cutaway, Finned Tube Bundle-Type is a professionally crafted, heavy-duty, durably coated, and fully detailed teaching aid that will provide years of service in the training lab or classroom. Be sure to check out DAC Worldwide’s website to explore a wide variety of other hands-on cutaways that feature the real-world components workers will encounter in the field!
- Published in News
Focused Training Key For Industry
Is the pandemic over? Some days it’s difficult to tell, as the ripple effects of continued cases of COVID-19 continue to pop up and create problems for both workers and manufacturers. Although the severity of pandemic-related disruptions has certainly subsided, industries around the world are still struggling with the aftershocks of a tumultuous few years.
In addition to ongoing supply chain woes, manufacturers are also contending with a labor marketplace that has changed fundamentally as a result of the pandemic. Prior to the pandemic, industry was struggling to fill open positions with qualified workers. Today, these struggles remain and in many areas have gotten even worse.
As a result, industries are placing a great emphasis on skills assessment to ensure that new hires can hit the ground running. In addition, upskilling current employees has taken on new significance, as industries seek to make the most of available human resources when it’s difficult to hire qualified new workers.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the current skills gap, the type of skills assessment and training that industry needs, and how the training tools offered by DAC Worldwide can help employers and instructors assess and train workers for the jobs of today and tomorrow.
How Wide is the Skills Gap?
Now that the worst of the pandemic appears to be behind us, things should be slowly getting better, right? Why then do manufacturers seem to be falling farther behind? According to an article by Alexandra Johnson:
“Before COVID, the situation was bad, but post-pandemic it has become even worse. Despite lockdown lifting, the industry is reporting over 515,000 jobs need filling, just to meet demand.”
Commonly known as the “skills gap,” there remains a sizeable disparity between the supply of highly-skilled workers and the demand for these workers in today’s industrial labor market. In fact, experts predict the skills gap is going to get even worse in the foreseeable future.
A study conducted by Deloitte for the Manufacturing Institute estimates that, over the next decade, almost 4.6 million manufacturing jobs will need to be filled. However, because of the skills gap, as many as 2.4 million — more than half! — of those jobs could go unfilled.
In a recent Forbes article, author Graham Glass notes that “[n]early half (46%) of learning and development (L&D) leaders say the skills gap is widening in their organization, and 49% say executives are concerned employees don’t have the right skills to execute business strategy, per findings from LinkedIn Learning’s ‘2022 Workplace Learning Report.’”
What is industry to do? Glass advises that “organizations need to emphasize employee upskilling, reskilling and right-skilling — and anticipate the skills employees need to succeed in their positions…By assessing the business’s needs pre-training (to develop training content) and post-training, companies can work to bridge skills gaps and create training programs that are impactful and useful to employees and the organization alike.”
Skills-Based Hiring
What’s the best approach for industry to take to bridge the skills gap? Should industry simply hire anyone they can get their hands on and then train them to do the jobs they need done? For many reasons, that strategy is probably not the best solution.
Industry is already struggling with a host of issues left over from the pandemic. Most companies don’t have the bandwidth to babysit new workers while they acquire the training they need. Many also don’t have either the personnel or the tools to effectively train new workers.
That’s why, in an article in the Harvard Business Review, LinkedIn CEO Ryan Roslansky advocates for a new skills-based approach to hiring. Roslansky urges employers to “[f]ocus on the results you’d like to see, rather than the type of qualifications that you think could deliver them. Highlighting the desired skills — the candidate’s ability to perform certain tasks — gets to the same results without creating an unnecessary barrier to entry, like a requirement for a four-year degree.”
In an article by Adina Miron, the author agrees:
“Skills-based hiring enables employers to hire for the skills gaps that exist within their organization. Rather than focusing on experience, education, or certifications, companies should focus on identifying candidates with the needed skills to fill open positions.”
Roslansky echoes these thoughts:
“Shifting to a skills-focused approach is a viable solution to an evolving workforce dilemma…Stay focused on skills — and the assessments that can measure them…there are plenty of ways to gauge a candidate’s ability to perform without relying on their education or experience as proxies.”
How do employers shift to a skills-based hiring approach? Unfortunately, generalized assessments and comprehensive training systems can be difficult to use in the context of hiring new workers in industry. Why? The answer can be found in the concept of specialization of labor.
According to an article by Sampson Quain:
“Specialization of labor…refers to a process in business in which large tasks are divided into smaller tasks, and different employees or different groups of employees complete those tasks. Specialization is highly desirable in large-scale operations such as…manufacturing because it allows workers with specific skill sets to efficiently perform a specific task.”
For example, a manufacturer may need to hire someone with a specific skillset related to the operation, maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair of mechanical belt drives. A prospective candidate might claim to have general mechanical knowledge and skills, but how can the employer know whether the worker has the specific belt drive skills it needs?
To effectively use a skills-based hiring approach in manufacturing, employers need focused assessment and training tools that can be used to adequately determine a potential worker’s skills in a very specific area.

Training at the Speed of Industry
Industry must also dedicate resources to ongoing training for current workers. The need for ongoing training is real and cannot be ignored. Industries today need to attack the skills gap with a combination of skills-based hiring and instituting training of current workers that is practical and effective.
In his Forbes article, Glass argues that “a personalized approach to training can also be useful to employees and companies.” However, he acknowledges that, “[i]n large companies, especially, creating individualized learning paths manually can be time- and resource-intensive.” He also points out that “employees need training that fits into their workflows.”
Most companies cannot afford the luxury of sending workers off-site for a week or more at a time for in-depth training. Instead, they need focused, skills-based training that allows workers to obtain the hands-on skills they need while minimizing the effect on production of time away from the workplace.
Fortunately, a variety of training tools exist that can offer industries time-saving, cost-effective solutions for focused skills assessment and hands-on training. In the next section, we’ll take a closer look at DAC Worldwide’s range of single-topic trainers that can help industry move to a skills-based hiring model and also upskill current employees.
DAC Worldwide Offers Focused Assessment & Training Tools
DAC Worldwide offers training systems for a variety of industry sectors, including advanced manufacturing, process/chemical manufacturing, marine, military, oil and gas, and power generation. These training systems also cover many different technical topics, such as electrical and electronics; heat transfer and steam; mechanical drives; oil production; process control and instrumentation; and pumps, compressors, and valves.
Rather than broad-based training in multiple areas, DAC Worldwide’s training systems provide hands-on training focused on specific tasks. This makes them particularly helpful to employers for skill assessment (either pre-employment or for upskilling purposes). For example, DAC Worldwide offers training systems targeted specifically at key mechanical maintenance skills:
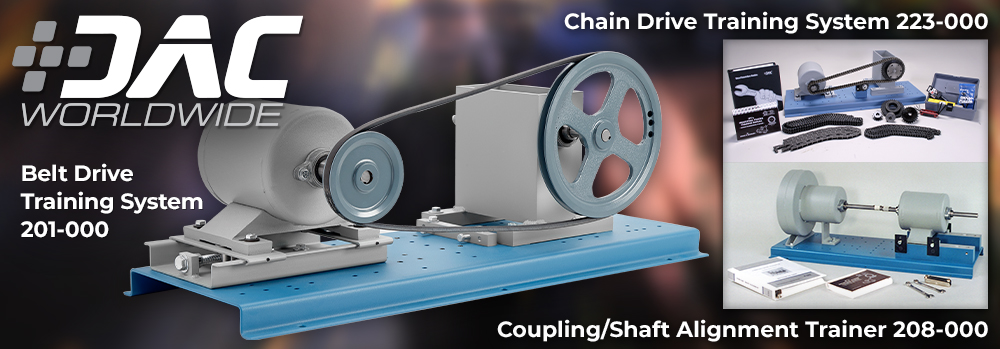
Belt Drive Training System
The Belt Drive Training System (201-000) allows for convenient assessment and training in the identification, installation, tensioning, and alignment of common belt drives types found in industry. Featuring hardware for applications related to multiple matched belts, fractional horsepower belts, positive drive belts, and variable pitch sheaves, the system provides a variety of training and assessment applications in one benchtop piece of equipment.
Coupling/Shaft Alignment Trainer
The Coupling/Shaft Alignment Trainer (208-000) allows for realistic training and assessment in shaft alignment. Designed based on the dimensions of a common ANSI centrifugal pump, this trainer can assess and train workers on all common alignment techniques and tools. Training and assessment topics include using a dial indicator in coupling/shaft alignment, the reverse dial indicator method, fabrication of shaft keys, and installing a flexible disc coupling.
Chain Drive Training System
The Chain Drive Training System (223-000) allows for in-depth assessment and training in industrial chain drives, heavy/silent chains, and sprocket set usage. Using industry-standard components workers will encounter on the job, this training system provides a complete training and assessment experience covering topics such as taper lock bushings, chain drive maintenance, installation/alignment of chains, and tensioning of chains.
Let DAC Worldwide Help You Fill Your Skills Gaps
The mechanical assessment and training tools highlighted above are just a few examples of the variety of technical training tools DAC Worldwide manufactures. In addition to training systems, DAC Worldwide also offers a wide range of industrial cutaways, detailed scale models, and sample boards featuring industrial components.
Contact a consultant with DAC Worldwide today to learn more about how their technical training tools can help you build the assessment and training program your company needs. Using DAC Worldwide training and assessment tools, you can transition to a skills-based hiring approach and fill the skills gaps in your organization!
About Duane Bolin
Duane Bolin is a former curriculum developer and education specialist. He is currently a Marketing Content Developer in the technical training solutions market.
- Published in News
Recognizing Red Flags: Training Workers to Prioritize Safety
Do you keep an eye out for red flags? If you’re still looking for that someone special, you might see red flags when their online dating profile indicates they’re unemployed and still living in their parents’ basement.
But those aren’t the red flags we’re talking about in this article. Red flags signify danger. They’re warning signs, and today’s workers need to recognize them in the workplace. Why? Their safety and wellbeing depends upon it.
Workplace safety remains a critical component of any industry’s success, yet it too frequently doesn’t get the attention it deserves. New technologies and the latest and greatest advances tend to capture the most attention, but the basics of safety can bring everything to a grinding halt if they’re ignored.
In this article, we’ll take a look at five red flags that workers must learn to recognize in order to make safety a top priority. We’ll also explain the importance of safety training and how the training tools offered by DAC Worldwide can help workers learn the skills that will keep them safe in the modern workplace.
5 Safety Red Flags Employees Must Learn to Recognize
How important is worker safety in your workplace? According to an IndustryWeek article by Matt Thiel and Dan Idzikowski, “nearly all [manufacturers] will say [safety is] a top priority…At the same time, the features and processes intended to keep people safe are rarely put to the test until a crisis occurs. It’s only when safety fails — when there is an injury or a near-miss — that companies question whether they are doing enough to protect workers.”
Modern industrial workplaces feature a wide variety of safety features designed to keep workers safe. Yet, workplace injuries remain a serious problem. For example, “more than 420,000 manufacturing workers were injured on the job in 2019, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, accounting for 15% of all nonfatal injuries in the private sector that year.”
What can be done to improve workplace safety? According to Thiel and Idzikowski, “[s]afety planning starts by imagining the unimaginable…it’s critical to play devil’s advocate and ask what could happen that shouldn’t, and how both the equipment and the operator will respond if it does.”
Once safety risks are identified, workers must be trained to recognize situations in which particular care must be taken to avoid injury. Otherwise, “[w]hen safety is treated as an afterthought, it’s only a matter of time until a preventable accident happens.” Here are five specific red flags Thiel and Idzikowski belive workers must learn to recognize:
- Access: Workers must learn to recognize situations in which “[o]perators can access hazardous areas while the hazard is present. Systems that require hands-on operator involvement…have built-in risks…Making these systems safe may mean containing the hazard behind guards or designing the machine so it won’t run until the operator is clear. Whether the danger is readily apparent, like moving parts, or invisible, like electrical current, the best safeguards make it impossible for the operator to even get near.”
- Rules: Workers should be on high alert for situations in which “[p]eople are bypassing the rules.Safety depends on people choosing to follow the rules…Even well-trained people can be lulled into a false sense of security and start taking shortcuts to make work faster or easier…If people are looking for ways around a safety system, it’s probably not well aligned with the operation. Rather than disabling the mechanism or retraining the operators, analyze the entire system and find a way to marry safety with the way the process really works.”
- Alarms: Workers need to notify management when “[a]larm systems don’t distinguish between emergencies and non-emergencies…if the system treats everything like an emergency, workers will treat nothing like an emergency. Frequent false alarms will lead workers to ignore the warning signs or circumvent them.”
- Obsolete: Workers must learn to keep an eye out for “[s]afety features [that] are outdated.A test of older fail-safes may find they no longer work — if they ever did in the first place…Maintaining a safe work environment means ongoing risk assessment. Safety professionals should perform regular audits of the equipment on the shop floor and keep an eye out for advancements that could make it safer.”
- Routine: Workers should alert management when they notice that “[s]afety features are not regularly tested and validated…the systems that keep workers safe should be checked on a regular basis.”
If workers can learn to recognize these five red flags, safety will become a higher priority and everyone in the workplace will benefit. As Thiel and Idzikowski acknowledge, “[t]he return on investment in safety is hard to measure. If a company invests millions in safety upgrades and there are no near-misses, was it a waste of money or did the upgrades do their job? A better question is what might realistically happen without safety upgrades.”
Safety Training: Begin with the Basics
Basic safety procedures are essential to keeping employees from becoming injured on the job. While manufacturing jobs can be dangerous, instituting safety procedures and ensuring that employees are properly trained are critical steps that employers must take to minimize the risk of injuries or death.
Not only does proper safety training reduce the number of workplace injuries, but it also adds to a company’s bottom line by improving productivity and reducing downtime caused by employees who can’t work when injured. But where should an employer start? How about at the beginning?
One of the most basic—and important—areas to focus on is the control of hazardous energy, often known by its more popular moniker “lockout/tagout.” According to the United States Department of Labor’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), “[e]nergy sources including electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, chemical, thermal, or other sources in machines and equipment can be hazardous to workers. During the servicing and maintenance of machines and equipment, the unexpected startup or release of stored energy can result in serious injury or death to workers.”
“Workers servicing or maintaining machines or equipment may be seriously injured or killed if hazardous energy is not properly controlled…Injuries may include electrocution, burns, crushing, cutting, lacerating, amputating, or fracturing body parts… Craft workers, electricians, machine operators, and laborers are among the millions of workers who service equipment routinely and face the greatest risk of injury.”
Fortunately, “[p]roper lockout/tagout (LOTO) practices and procedures safeguard workers from hazardous energy releases.” Teaching workers hands-on LOTO skills will help them to understand how to properly control hazardous energy and maintain a safe work environment.
DAC Worldwide Offers Superior LOTO Training
For companies looking to improve their safety training, a thorough review of current training materials is a great place to start. Do employees have access to hands-on training with actual components they’ll encounter on the job? If not, partnering with established companies to provide industrial-quality training systems that will stand the test of time will help ensure the continued safety of the workforce.
Employers don’t need to recreate the wheel to move toward a skills-based approach to hiring. DAC Worldwide, an industry-leading manufacturer of technical assessment and training tools, offers a variety of solutions to the problems employers face.
For example, DAC Worldwide offers a safety training system specifically designed to give employees the hands-on experience they need to master lockout/tagout skills. DAC Worldwide’s Lock-Out/Tag-Out Training System (811-000) features a realistic, simulated working process environment that facilitates introductory training with hands-on activities related to the process of identifying and locking out sources of dangerous potential energy in an industrial setting.
Since technical training is most effective when learners can gain hands-on practice with industry-standard components they’ll encounter on the job, the Lock-Out/Tag-Out Training System features a wide variety of common, industrial-quality components to provide learners with a realistic training experience that will build skills that translate easily to the workplace.
For example, the Lock-Out/Tag-Out Training System features:
- two PVC process tanks with removable covers, vents, drains, and process connections;
- PVC process network with block valves, 3-way valves, figure-8 blinds, and descriptive valve tags;
- fractional HP magnetic drive centrifugal pump;
- drain collection and distribution tubing network with valved central collection manifold;
- electrical controls, with provision for lock-out, including primary service disconnect, motor starter switch, in-line GFI protector, and system plug connection; and
- a comprehensive lock-out/tag-out tool kit with color-coded locks, tags, multi-lock hasps, specialty electrical locking devices, valve locking devices of multiple designs, and a dedicated toolbox.
The Lock-Out/Tag-Out Training System’s courseware consists of a training manual and hands-on exercises. These can be used as part of either an instructor-led course or self-directed study. A final performance assessment exercise is also provided, allowing the system to be used in an alternate configuration for testing purposes.
Contact a consultant with DAC Worldwide today to learn more about how their technical training tools can help you build the assessment and training program your company needs. Using DAC Worldwide training and assessment tools, you can transition to a skills-based hiring approach and fill the skills gaps in your organization!
- Published in News
What is Process Technology and why is it so important right now?
Process technology employees in the United States are the highly skilled operators of oil refineries, and the positions they hold require distinct training. Process technicians are responsible for monitoring and maintaining the production processes in a facility. They monitor equipment, operation, and safety systems, and are occasionally involved in the installation and repairing of equipment, like pumps, compressors, and electric motors. Students pursuing a career in process technology can often expect a good salary, job advancement opportunities, and an interesting, sometimes challenging, role using technology in manufacturing.
What is going on in the oil production industry?
Despite slowing growth, US oil production is on track to reach and all-time high in 2023. Output is expected to expand at an average rate of 840,000 barrels a day next year, down from a prior forecast of 860,000, according to the Energy Information Administration.
A reduction in supply from the United States could exacerbate an already fraught situation, in the midst of Vladimir Putin’s invasion of Ukraine, and subsequent sanctions and trade embargos. Previously the US was relied upon as a key ancillary producer, that can subsidize the global supply as demand increases. The US has an immediate need for properly trained Oil Industry professionals, in order to ramp up domestic oil production.
In an effort to attract the skilled workforce of the future, The American Petroleum Institute (API) announced a new initiative encouraging veterans and transitioning service members to apply their skills in the oil and gas industry. Per worldoil.com; ‘participants obtain professional credentialing through API’s Individual Certification Programs (ICP).’ API plans to develop additional programs and tools to help transitioning service members and veterans. More information can be found here.
A great deal of workers left the Oil industry following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Currently, there are still roughly 100,000 fewer oil and gas workers now in the country than before the pandemic despite the U.S. unemployment rate has falling to 3.6%, slightly above the pre-pandemic low. Companies such as Patterson-UTI raised wages last year because of competition from retailers that historically paid less than the oil industry.
Rystad forecasts that U.S. oil and gas employment is expected to recover this year (2022), and surpass pre-pandemic figures to an oilfield workforce of almost 1.1 million by the end of 2027. By the end of this year, U.S. oil and gas employment is expected to expand 12.5% to almost 971,000.
Specialized workers are key to restoring the workforce needed to ramp up production. DAC Worldwide’s process control and instrumentation products provide hands-on training for multiple tasks including those associated with flow, level, and temperature controlled processes.
DAC Worldwide’s Vertical Separator Trainer (295-101) is a reduced-scale, three-phrase vertical separator that mimics its real-world counterpart by using alternate production stream components, refined oil, air, and water.
https://dacworldwide.com/product/vertical-separator-trainer/
DAC Worldwide’s Vertical Separator Training System Plus (295-101-PAC) is a realistic working demonstration separation system duplicates the process at a reduced scale using alternate production stream components: refined oil, air, and water. Three-phase separators, both vertical and horizontal, perform a fundamental purpose in oilfield production operations. Using very basic physical principles of gravity separation, the device efficiently separates mixed raw oil and gas production streams into their component parts: crude oil, gas, and water.
https://dacworldwide.com/product/vertical-separator-training-plus/
More Oil and Gas training solutions from DAC can be found here.
- Published in News
Fundamental Electrical Skills Training: Powering the Path to Success
No matter their experience, skill level, or desired specialty, all individuals aspiring to become electrical professionals need the same fundamental electrical skills. These include understanding the basic principles of electricity and working with common electrical components, such as wiring, motors, and circuits. By mastering core skills like these, learners can help ensure they work safely and efficiently in whatever specified path they choose, whether that is industrial, commercial, or residential electrical careers.
As with any discipline, learning fundamental skills establishes a foundation from which a learner can build more complex concepts and skills. An electrician who now wires entire buildings for manufacturing processes was once a student learning about electric current. Furthermore, that same electrician could choose to expand their skills into more advanced or niche areas, such as performing industrial maintenance for the robotic arms they run power to, which would require that they rely on their understanding of basic PLC operation to progress to the complex coding needed to ensure manufacturing level precision.
Additionally, an electrical technician’s understanding of basic concepts and their abilities helps build confidence that translates to efficiency. For example, an HVAC technician is able to quickly restore air conditioning to a home because they understand how the circuit board, fan motor, compressor, and other components work both individually and together to create a working system. However, if the technician did not have a knowledge of wiring practices, the job would move much more slowly and, if done wrong, could even be dangerous.
In the same vein, industrial workers that know the do’s and don’ts of electrical practices can help recognize and prevent risky electrical setups. This makes a workplace safer for everyone and can help a company avoid downtime. In essence, fundamental electrical skills help prepare future technicians of many career paths to handle any job they will face in the field and provide the first step in pursuing a successful career in the electrical field.
DAC Worldwide’s Electrical Training Systems
DAC Worldwide offers many training systems that teach learners the fundamental electrical skills they need for a successful career. Each trainer is compact and sturdy, allowing for ease of relocation and longevity of use. By using these systems, learners will practice crucial hands-on skills related to focused electrical topics. Below, we’ve included a sampling of our most popular electrical trainers.
400-PAC – Modular Basic Electricity Training System Plus
The 400-PAC covers basic AC and DC electrical principles, including installation, operation, and troubleshooting for multiple applications. Learners can expect to gain a greater understanding of how electricity is used for power and control in industrial, commercial, and residential settings.
This trainer uses 43 activities to engage learners in lessons covering topics such as terminology, background theory, component examination and testing, circuit design, and more. A built-in circuit breaker, transformer, and internal power supply create working voltages of 24VAC/24VDC. This allows learners to gain hands-on experience with skills like calculating and regulating voltage in a circuit, operating a clipper circuit and full-wave bridge rectifier, loading dry cells, utilizing indicator lamps and toggle switches, and much more.
420-000 – 1-Phase Motor Control Training System with Manual Starter
The 420-000 is a single-topic trainer that allows learners to focus solely on navigating the operation, wiring, troubleshooting, and application of an industrial single-phase AC motor with a manual starter. With redundant safety systems provided and a keyed instructor power switch, learners can safely study individually or in small groups.
 The system also comes equipped with a motor, manual motor starter, circuit breaker, electrical interlock, pilot light, e-stop switch, and four instructor fault switches. Learners use shielded banana-jack connections to wire the motor. While self-contained, the trainer may be expanded with supplemental components, such as a piloting switch module and a motor loading device, to teach additional topics.
The system also comes equipped with a motor, manual motor starter, circuit breaker, electrical interlock, pilot light, e-stop switch, and four instructor fault switches. Learners use shielded banana-jack connections to wire the motor. While self-contained, the trainer may be expanded with supplemental components, such as a piloting switch module and a motor loading device, to teach additional topics.
422-000 – 3-Phase Motor Control Training System with Manual Starter
Like the 420-000, the 422-000 is a self-contained, single-topic trainer that allows for independent or small group study. Multiple components, such as a keyed instructor power switch, permanent internal grounding, circuit breaker with lock-out/tag-out, and a large emergency stop switch, ensure learner safety. All equipped components are UL and CE certified.
This trainer offers 21 activities for learners to practice hands-on skills for operating, wiring, and troubleshooting an industrial three-phase AC motor with a manual starter. Some examples of these skills include wiring a three-pole pushbutton motor starter as a motor controller and employing the instructor fault switches to troubleshoot a drum-type reversing switch manual starter.
429E – AC Variable Frequency Drive Training System Plus
The 429E uses industrial-grade components, such as an industrial 3-phase motor and an Allen-Bradley PowerFlex 40 variable frequency drive, to teach AC drive programming, system troubleshooting, control wiring, and other industry-relevant skills. Various inputs and outputs and a programmable acceleration/deceleration with an on-board PID control loop allow learners further practice in understanding voltage, relay, resistance, and amperage.
Other course content includes topics like minimum and maximum frequency, jog parameters, skip frequency bandwidth, and checking and setting acceleration and deceleration timing. Eight fault insertion switches provide thorough real-time troubleshooting practice.
461-000 – Basic PLC Training System (AB Micro850)
The 461-000 provides a wealth of information for learners to develop a firm understanding of industrial PLCs, with emphasis on the current generation Allen-Bradley Micro850. This trainer features eight DC input switches, eight DC output LED lights, two 25-pin D-Sub input/output connectors, multiple safety components, and more. Eight fault insertion switches are also built into the system to help learners increase their proficiency with PLC troubleshooting.
An optional textbook offers more study for relevant topics, such as introducing Boolean algebra and Veitch diagrams, understanding logic gates, creating subroutines and sequencers, and much more. The trainer can also be expanded by connecting it to other training systems that teach process control, sensors, motor control, fluid power, and more.
Boost Your Electrical Training Program Today
We aim to make training more memorable and effective so future electrical technicians can thrive in their chosen career paths. For more information on which training aide may best fit your needs, contact a DAC Worldwide consultant today.
- Published in News
Focused Assessment Key to Finding Workers with the Right Skills
Click HERE to view Focused Assessment Key to Finding Workers with the Right Skills as a multimedia presentation.
“Now Hiring!”
These days, it seems like it doesn’t matter what type of business you’re in. If your business is open, then it probably has one of these signs in the window.
As industries across every sector continue to navigate the ups and downs of an uneven economic recovery in the wake of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, hiring managers are struggling to fill open positions.
Whether you’re an employer looking to fill critical roles or an instructor trying to prepare your students for available jobs, it’s important to understand that now, more than ever, workers need the right skills to be successful in the modern industrial workplace.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the issues employers face trying to find workers with the right skills. We’ll also explain the importance of focused assessment and how the training tools offered by DAC Worldwide can help employers and instructors assess and train workers for the jobs of today and tomorrow.
Why are there so many Open Manufacturing Jobs?
 The COVID-19 pandemic took a heavy toll on manufacturers. Combining fluctuating demand with quarantining workers and vast supply chain disruptions, many manufacturers struggled to weather the many storms they faced.
The COVID-19 pandemic took a heavy toll on manufacturers. Combining fluctuating demand with quarantining workers and vast supply chain disruptions, many manufacturers struggled to weather the many storms they faced.
Now that we’re in an extended period of uncertain recovery, things should be slowly getting better. After all, unemployed people do need jobs, right? Instead, manufacturers seem to be falling farther behind.
According to an article by Alexandra Johnson:
“The US manufacturing industry is forecast to grow 7% in 2021, yet with this anticipated growth, the industry is struggling to hire enough workers to meet demand. Before COVID, the situation was bad, but post-pandemic it has become even worse. Despite lockdown lifting, the industry is reporting over 515,000 jobs need filling, just to meet demand.”
Why are so many manufacturers having such a hard time filling their many open positions? Experts believe that a big part of the problem is that too many workers simply don’t possess the skills employers need.
Today’s manufacturing workplace isn’t the dirty, boring, repetitive assembly line some people erroneously imagine. Modern facilities feature cutting-edge technologies that require specialized skills that not enough workers seem to have these days.
How can Manufacturers find Workers with the Right Skills?
With so many open positions to fill, it might seem like manufacturers should simply hire anyone they can get their hands on and then train them to do the jobs they need done. This approach, however, isn’t advisable for a variety of reasons.
Primarily, manufacturers who are already struggling with a whole host of issues don’t have the bandwidth to babysit new workers while they acquire the training they need. Many manufacturers also don’t have either the personnel or the tools to effectively train new workers.
In an article in the Harvard Business Review, LinkedIn CEO Ryan Roslansky advocates for a new skills-based approach to hiring. Roslansky argues that a skills-based approach “is the future of hiring and development…At a time when talent is the number-one commodity in business, companies can’t afford to remain stuck in old mindsets.”
Roslansky urges employers to “[f]ocus on the results you’d like to see, rather than the type of qualifications that you think could deliver them. Highlighting the desired skills — the candidate’s ability to perform certain tasks — gets to the same results without creating an unnecessary barrier to entry, like a requirement for a four-year degree.”
In an article by Adina Miron, the author agrees:
“Skills-based hiring enables employers to hire for the skills gaps that exist within their organization. Rather than focusing on experience, education, or certifications, companies should focus on identifying candidates with the needed skills to fill open positions.”
Roslansky echoes these thoughts:
“Shifting to a skills-focused approach is a viable solution to an evolving workforce dilemma…Stay focused on skills — and the assessments that can measure them…there are plenty of ways to gauge a candidate’s ability to perform without relying on their education or experience as proxies.”
A Skills-Based Hiring Approach Requires Proper Assessment & Training Tools
 The nature of manufacturing makes generalized assessments and comprehensive training systems difficult to use in the context of hiring new workers. Why? The answer can be found in the concept of specialization of labor.
The nature of manufacturing makes generalized assessments and comprehensive training systems difficult to use in the context of hiring new workers. Why? The answer can be found in the concept of specialization of labor.
According to an article by Sampson Quain:
“Specialization of labor…refers to a process in business in which large tasks are divided into smaller tasks, and different employees or different groups of employees complete those tasks. Specialization is highly desirable in large-scale operations such as…manufacturing because it allows workers with specific skill sets to efficiently perform a specific task.”
For example, a manufacturer may need to hire someone with a specific skillset related to the operation, maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair of mechanical belt drives. A prospective candidate might claim to have general mechanical knowledge and skills, but how can the employer know whether the worker has the specific belt drive skills it needs?
To effectively use a skills-based hiring approach in manufacturing, employers need focused assessment and training tools that can be used to adequately determine a potential worker’s skills in a very specific area.
DAC Worldwide Offers Focused Assessment & Training Tools
Employers don’t need to recreate the wheel to move toward a skills-based approach to hiring. DAC Worldwide, an industry-leading manufacturer of technical assessment and training tools, offers a variety of solutions to the problems employers face.
In this section, we’ll take a closer look at several of DAC Worldwide’s focused assessment and training tools that employers can use to effectively and efficiently ensure that they’re hiring workers with the skills they need.
 Belt Drive Training System (Model: 201-000)
Belt Drive Training System (Model: 201-000)
The Belt Drive Training System allows for convenient assessment and training in the identification, installation, tensioning, and alignment of common belt drives types found in industry. Featuring hardware for applications related to multiple matched belts, fractional horsepower belts, positive drive belts, and variable pitch sheaves, the system provides a variety of training and assessment applications in one benchtop piece of equipment.
Coupling/Shaft Alignment Trainer (Model: 208-000)
The Coupling/Shaft Alignment Trainer allows for realistic training and assessment in shaft alignment. Designed based on the dimensions of a common ANSI centrifugal pump, this trainer can assess and train workers on all common alignment techniques and tools. Training and assessment topics include using a dial indicator in coupling/shaft alignment, the reverse dial indicator method, fabrication of shaft keys, and installing a flexible disc coupling.
Chain Drive Training System (Model: 223-000)
The Chain Drive Training System allows for in-depth assessment and training in industrial chain drives, heavy/silent chains, and sprocket set usage. Using industry-standard components workers will encounter on the job, this training system provides a complete training and assessment experience covering topics such as taper lock bushings, chain drive maintenance, installation/alignment of chains, and tensioning of chains.
 Let DAC Worldwide Help You Fill Your Skills Gaps
Let DAC Worldwide Help You Fill Your Skills Gaps
The mechanical assessment and training tools highlighted above are just a few examples of the variety of technical training tools DAC Worldwide manufactures. In addition to training systems, DAC Worldwide also offers a wide range of industrial cutaways, detailed scale models, and sample boards featuring industrial components.
Contact a consultant with DAC Worldwide today to learn more about how their technical training tools can help you build the assessment and training program your company needs. Using DAC Worldwide training and assessment tools, you can transition to a skills-based hiring approach and fill the skills gaps in your organization!
- Published in News
Pump It Up! A Primer on the Importance of Pump Maintenance
When you hear the phrase, “pump the jam” your mind could be drawn – if you are of a certain age – to Technotronic’s 1989 club hit “Pump Up the Jam.” But you could also be a machine operator in a jam factory where pumps are used in the production process and must be routinely maintained due to jam viscosity, seeds and fruit chunks, and the sugary buildup on seal faces in sealed pumps.
In addition to jam factories, pumps are used across industry for water movement, chemical processing, and fluid management, as well as for moving harsh, corrosive, or heavy-duty substances. These fundamental components are utilized in agriculture, food and beverage, mining, petroleum, power generation, and pharmaceutical applications to move everything from wastewater to petroleum, sludges to slurries, dairy products to wine, and on and on. Pumps come in an assortment of types and configurations and industry uses a variety of them, such as turbine, piston, and gear pumps.
The most widely used pump across industry is the centrifugal pump, which is a dynamic pump, meaning it adds kinetic energy to the substance that increases the fluid speed and creates pressure. As expected with any kind of mechanical component subjected to constant pressure and operation, wear and tear of pumps is inevitable. However, with a solid understanding of the most common problems occurring from prolonged pump operation and a routine maintenance plan, full scale pump failure and costly production shut downs can be avoided. The most prominent problem with pumps that routine maintenance can prevent is cavitation.
What is Cavitation?
In relation to pumps, cavitation is the phenomena where vacuum bubbles form within fluid being moved through a system. When these bubbles – or voids – collapse they create shockwaves. Over time and repeated use, these shockwaves create premature wear on a pump impeller and lead to component failure if no maintenance is performed. Not only does cavitation lead to component failure, but when present it is extremely noisy and causes vibrations, which results in a loss of process efficiency.
In addition to cavitation, common things that technicians should watch for on industrial pumps include bearing and lubricant condition, shaft seal condition, pump vibration, and pump discharge pressure.
What Pump Maintenance Tasks Can Prevent Cavitation and Pump Failure?
As with any machine, consistent maintenance is key to process efficiency and prevention of equipment failure. In pumps, maintenance can extent equipment life, decrease operating and costs, and prevent specific component ills like cavitation. Generally, it’s recommended to group your maintenance program into three categories: routine, quarterly, and annual. Examples of tasks to track and check include adding oil to the bearing reservoir, cleaning and oiling governor linkages and valve stems, and inspecting disc couplings.
But how can you ensure that maintenance technicians and operators at your facility have the know-how to perform these tasks correctly?
DAC Worldwide’s Pump Maintenance and Operation Training Systems
DAC Worldwide offers an array of options for up-skilling or assessing your employees for pump maintenance and operation, including:
Centrifugal Pump Fundamentals Training System Plus (227-PAC)
The Centrifugal Pump Fundamentals Training System Plus (277-PAC) offers hands-on training for basic centrifugal pump operation and maintenance. This system can be used to demonstrate pump cavitation, fundamental operational principles, and the effects on flow and pressure by varying static head and piping configuration. The Centrifugal Pump Fundamentals Training System is a perfect solution for introductory operations and maintenance courses related to centrifugal pumps and process systems.
This system features a centrifugal pump with an open impeller, a variable speed DC pump motor with a controller, and a modular, clear PVC piping system with a variable-height support structure that allows for multiple configurations of the tank, pump, and motor to create new flow and static head conditions. The system also offers optional pipe spool variations to create even more process flow conditions.
Pump Maintenance Training System Plus (275-PAC)
DAC Worldwide’s Pump Maintenance Training System Plus (275-PAC) is a benchtop training device featuring a standard ANSI centrifugal pump mounted on a heavy-duty, 7-gauge, formed-steel, powder-coated baseplate. This systems features real-world pump components for practicing the disassembly, packing, and reassembly of common centrifugal pumps, as well as common pump maintenance such as impeller clearance adjustment and mechanical seal replacement. This system also features a clear acrylic backhead for visibility of the seal area.
Pump Maintenance and Alignment Training System Plus (275E-PAC)
The Pump Maintenance and Alignment Training System Plus (275E-PAC) is a benchtop training system featuring a standard ANSI centrifugal pump and a simulated motor element. This combination along with a replaceable ¾-in. diameter steel shaft with keyways allows users to practice shaft alignment skills. Further, the motor element features flanged bearings that can be adjusted to allow for angular and parallel misalignment. This system also allows users to practice complete pump tear-down and assembly. The Pump Maintenance and Alignment Training System also features a clear acrylic backhead to show pump packing procedures and the installation of mechanical seals.
Additionally, DAC Worldwide has dissectibles, component cutaways, and sample boards for expanded industrial pump training. DAC’s sister company, Amatrol, also offers pump systems that can bolster your industrial training program.
Amatrol’s Centrifugal Pump Learning System (950-PM1) and Expansion Systems
Amatrol’s pumps learning systems cover industry-relevant skills including how to operate, install, maintain, troubleshoot, and select a variety of pumps, as well as system design. The base learning system features a centrifugal pump, but allows for the use of several different pumps for expanded training; these pumps include: parallel pumps, turbine pump, diaphragm pump, peristaltic pump, piston pump, gear pump, magnetic pump, and centrifugal pump with stuffing box.
- Published in News
DAC Worldwide’s 4-Variable Process Control System: The Ultimate Instrumentation Training Tool
Let’s say on the way to pick up you prescription at the drug store, you stop at the gas station, fill up your tank, and pick up a cold soda pop. By the time you get home, you’ve interacted with at least three products that use process control and instrumentation in their creation. Oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage are only three of the countless number of industries that rely on process control and instrumentation to produce their goods.
What is process control and instrumentation?
According to the Process Industry Informer’s Phil Black, “Process control is used in continuous production – in manufacturing and in other fields and industries where some kind of material is produced without any kind of interruption – as well as in ‘batch processing.’ It’s used to automatically control the conditions in which a product is made – ensuring better quality and efficiency.”
 And the applications of these processes are only getting started. According to Amatrol’s Duane Bolin, “Process control is big business all over the world. The global economic value of the process control systems market is estimated to be more than $120 billion. This value will only continue to grow as automation and Industry 4.0 technologies enable process control systems to further increase the productivity and efficiency of manufacturing facilities.”
And the applications of these processes are only getting started. According to Amatrol’s Duane Bolin, “Process control is big business all over the world. The global economic value of the process control systems market is estimated to be more than $120 billion. This value will only continue to grow as automation and Industry 4.0 technologies enable process control systems to further increase the productivity and efficiency of manufacturing facilities.”
Why is process control important?
Much like its applications, the importance of process control is nearly limitless in industry, but here are three major reasons:
-
Improved Process Efficiencies
Process control allows for improved process efficiencies because the data produced by sensors can be analyzed resulting in more effective decisions.
-
Limited Staff
Because processes can be automated, a small staff of operators can control the most complex processes from a central location.
-
Ensures Safety
Manipulating substances to produce a product is a very demanding and potentially hazardous process. The controlled environments and components within process control limit danger to operators.
How do I set up process control training for our school or industry training center?
So you have a workforce or classroom full of people that need to be upskilled on process control and instrumentation practices. Where do you begin? Technical training innovators like Amatrol, DAC Worldwide, Bayport, and Pignat offer a variety of concentrated, single-topic options for process control training like Amatrol’s Temperature (T5553) or Pressure (T5555) systems, DAC Worldwide’s Calibration Training (616-000) system, Bayport’s Flow Level Trainer (120-CFLCD), or Pignat’s Gas-Liquid Absorption (ABS/2000) system. However, there is one system that not only offers hands-on skill building across all forms of instrumentation training, but is also customizable to an almost limitless degree to exactly meet your training needs:
DAC Worldwide’s 4-Variable Advanced Process Control Training System (603-000)
DAC Worldwide’s 4-Variable Advanced Process Control Training System (603-000) allows candidates to build hands-on skills in flow, level, pressure, and temperature process control applications. This system features an open physical architecture and wiring design, which allows for incredible adaptability and customization. This system can be configured to meet almost any process control training need or industry application and allows you to modify it as needs or technology changes.
The large size of the system and more complex measurement and control environment enables for PLC and DCS control systems, which means it can be set up for one large complex loop or two individual loops. This system can also feature Hart, Foundation Fieldbus, and Profibus communication systems.
The DACW 4-Variable Advanced Process Control Training System can be used for everything from interpreting PNID drawings, to teaching system walkdowns and PID control methodology, to the creation and maintenance of instrument loops, as well as large-scale system troubleshooting. This instrumentation training system includes a dynamic and complex piping system with a PID on each side, which allows for experiments in true cascade control – a topic that is uniquely covered by the 603-000 in the technical training industry.
There are also instrumentation packages – including Endress Hauser, Rosemount, & Honeywell – available to fully meet the training needs that most closely resemble the equipment you’ll see in your company or local industry.
Even More Process Control Option from DAC Worldwide!
If 4-Variable Advanced Process Control Training System is a bit more than what your training program needs, DAC Worldwide offers a full line of process control and instrumentation options. Some of these include single-topic options such as Analytic Process Control (605-000), Temperature Process Control (602-PAC), and a PID Controller Trainer (608-000).
How Can DAC Worldwide Help Your Training Program?
With more than four decades of experience in industrial training, DAC Worldwide’s reach extends far beyond just electrical products. In fact, DAC Worldwide possesses knowledge and expertise in a wide range of technical topics, including Electronics, Fluid Power, Heat Transfer & Steam, HVAC, Machining & Measurement, Mechanical Drives, Oil Production, Process Control & Instrumentation, and Pumps, Compressors & Valves.
Our training aids range from training systems and sample boards, to models and dissectibles – with real-world, hands-on learning being the core of each product. For more information on how DAC Worldwide can enhance your industrial training program and provide you with the best training solutions available, please click here.
- Published in News
Staying Protected: Hands-On Transformer Training in Safe, Controlled Environment
To view a multimedia presentation of “Staying Protected: Hands-On Transformer Training in Safe, Controlled Environment”, please click here.
The life of a power line worker can be a precarious one. From maintaining interstate power grids to servicing transmission lines and towers, line workers are often tasked with jobs that aren’t for the faint of heart.
The profession is considered one of the most dangerous in America, with 35 fatalities in 2019 around the United States. The compensation for such an intimidating trade, though, is notable.
According to salary.com, the average lineman salary in the United States is $80,026, as of February 2021. The career offers very realistic expectations of making upwards of $100,000 annually before turning 25 for younger students.
Today, the career is becoming safer, thanks to developing safety technologies. There are Linemen Training Schools all over the United States and Canada, with many finding interest in the unique field of high-voltage electrical technology.
Despite the demands, it is critical for workers to be properly trained on the power that electricity holds, both physically and metaphorically. Due to its hazardous nature, becoming a lineman requires extensive technical knowledge and safety skills to help ensure worker safety.
In the past, teaching the ins and outs of transformers was primarily paper-based, with some programs even opting for full-voltage training. Most of the time, the “real” learning was done on-the-job.
But things have changed in the electrical technology field. Training future lineworkers no longer requires a book-only approach, or the dangers that come with full voltages. DAC Worldwide’s Transformer Connections Training System (413-000) is a utility worker training aid that provides learners with real-world, hands-on practice working with transformers.
What is the Transformer Connections Training System?
DAC Worldwide’s Transformer Connections Training System is the ideal training tool for any lineman training program. It replicates the on-site conditions and circumstances that a utility worker encounters when making common transformer connections in the field. It allows the student to learn with a “hands-on” approach in a comfortable and controlled classroom environment.
Gone are the days of full-voltage training and paper-based learning, as the training unit is internally fused and includes a recalibrated reduced-voltage meter to make training safe, efficient, and realistic. As students train on the system at 4100 VAC, for example, they will only be operating at 41 Volts. This allows them to see real line voltage without the potential of getting hurt.
Put together in a welded steel cabinet, the Transformer Connections Training System is wired for both single-phase and three-phase activities. It includes 14 transformer cans, which are wired with different configurations to allow for a variety of set-ups, as well as a panel-mounted voltmeter and a phase rotation meter. It requires a 208 VAC / 3-phase / 60Hz / 4-wire connection.
In addition to the hands-on approach, the Transformer Connections Training System includes a Student Training Manual with a variety of topics, like performing single-phase transformer connections, identifying 3-phase connections, and demonstrating how capacitors affect line voltage and current. Learners will also learn how to demonstrate parallel single-phase and 3-phase transformers, and other transformer-related topics and skills.
Other Transformer Training Products
In addition to the Transformer Connections Training System, DAC Worldwide also offers slightly different variation called the Transformer Wiring Training System (408-000). This training tool is ideal for future industrial electrical programs and electricians, as it covers a basic course on transformers. It can also be used in residential electrical programs, as the system also shows how to connect a residential service.
Like the 418-000, the Transformer Wiring trainer takes the safe approach in learning by using low-voltage outputs while simultaneously simulating high-voltages. It replicates the single-phase transformer connections, as well as both delta-wye 3-phase transformer connections. All of the transformers are the same, and build into the unit, with the middle representing six different generators.
Students will be able to demonstrate proper installation of ground connections, primary and secondary side connections, and parallel transformer connections. The system also includes eight built-in instructor fault switches, which simulate failure conditions and allow real-time assessment and troubleshooting for students.
In addition to training systems, DAC Worldwide also offers two Transformers cutaways: one depicting a single-phase transformer, with the other showcasing a three-phase. Cutaways are real-world industrial components that have been restored, cut away, and refinished using durable urethane coatings. Each of these industrial components has been professionally sectioned to expose each device’s primary components, with functionality completely retained.
The Single-Phase Transformer (273-912) highlights a common shell-type, single-phase transformer found in manufacturing facilities and refineries, among others. The Three-Phase Transformer Cutaway (273-915) features a common coaxially-wound, three-phase, delta-wye transformer found in various industrial and commercial applications.
How Can DAC Worldwide Help Your Training Program?
With more than four decades of experience in industrial training, DAC Worldwide’s reach extends far beyond just electrical products. In fact, DAC Worldwide possesses knowledge and expertise in a wide range of technical topics, including Electronics, Fluid Power, Heat Transfer & Steam, HVAC, Machining & Measurement, Mechanical Drives, Oil Production, Process Control & Instrumentation, and Pumps, Compressors & Valves.
Our training aids range from training systems and sample boards, to models and dissectibles – with real-world, hands-on learning being the core of each product. For more information on how DAC Worldwide can enhance your industrial training program and provide you with the best training solutions available, please click here.
- Published in News
Hands-On Training Essential for Nation’s Utility Workers
Click HERE to view Hands-On Training Essential for Nation’s Utility Workers as a multimedia presentation.
Do you ever daydream about going “off the grid”? For many, the thought of unplugging for an extended time away from life’s troubles sounds refreshing.
The reality underlying this common dream of escape is how thoroughly tied our lives are to the grid. What would our everyday routines be like without the utilities we so often take for granted?
We don’t give them much thought until Mother Nature intervenes with a foot of snow or an ice storm. When the lights go out, the Internet stops streaming, water freezes in the pipes, and furnaces quit heating, we think about nothing but our precious utilities until they return.
The unsung heroes in these situations are the nation’s frontline utility workers that must brave the elements to do their jobs in the worst circumstances. We wait anxiously and depend upon their expertise and dedication to restore our lives back to normal.
One day soon, though, we could find that wait lasting longer and longer. Why? Our nation’s utilities are facing an unprecedented — and worsening — shortage of workers with the skills necessary to keep the grid functional.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the looming shortage of utility workers across the country. We’ll also examine how one training center in Kansas is addressing the issue. Finally, we’ll discuss easy-to-use training options that any utility can use to provide safe, hands-on skills training to their frontline workers.
The Power & Utilities Skills Gap
 Industries of all kinds across the nation are facing a critical shortage of skilled workers, and the power and utility industries are no exception. Demand for workers in these industries remains strong, but finding new workers to replace the many workers ready to retire is proving to be a substantial challenge.
Industries of all kinds across the nation are facing a critical shortage of skilled workers, and the power and utility industries are no exception. Demand for workers in these industries remains strong, but finding new workers to replace the many workers ready to retire is proving to be a substantial challenge.
In an Energy Central article, author Karen Marcus notes:
“As older workers retire, many utilities are finding it difficult to replace them, and to attract employees with the skills needed to advance a 21st century industry. According to T&D World, Airswift and Energy Jobline found in a survey of over 17,000 professionals that ‘48 percent of power professionals are concerned about an impending talent emergency, with 32 percent believing the crisis to have already hit the sector and 38 percent reporting that their company had been affected by skills shortages.’”
The shortage of skilled workers is real, and experts predict it’s only going to get worse in the future. According to Marcus:
“The U.S. Department of Energy (DoE) Quadrennial Energy Review (QER) reports that, according to one study, the industry will ‘need 105,000 new workers in the smart grid and electric utility industry by 2030, but expects that only 25,000 existing industry personnel are interested in filling those positions.’ The remaining 80,000 employees in this supply-demand mismatch will need to be filled through recruiting and training. However, the industry is not expected to meet the forecasted need with its current recruitment and training rates.”
Obviously, something needs to change. As the DoE QER states, “Industry hiring managers often report that lack of candidate training, experience, or technical skills are major reasons why replacement personnel can be challenging to find.”
If the power and utilities skills gap is to be bridged, utility companies must find a way to effectively provide safe, hands-on training to equip current and future workers with the critical skills they need to fill frontline positions as quickly as possible. Fortunately, solutions are available, and in the next section we’ll examine an exemplary approach taken by an association of municipal utilities in Kansas.
A Training Pioneer
 Nearly two decades ago, Kansas Municipal Utilities (KMU), an association of more than 100 public utilities across the state of Kansas, recognized a dire need to effectively train the next generation of field workers. The groundbreaking solution KMU pioneered was finally brought to life a few years ago in the form of a $3.2 million training center.
Nearly two decades ago, Kansas Municipal Utilities (KMU), an association of more than 100 public utilities across the state of Kansas, recognized a dire need to effectively train the next generation of field workers. The groundbreaking solution KMU pioneered was finally brought to life a few years ago in the form of a $3.2 million training center.
As author Rick Aguilar notes in a T&D World article, KMU’s 20,000-square-foot training facility was seen as “a way to short-circuit the learning curve so utilities could swiftly prepare new hires to work as effective front-line employees.”
KMU’s training center allows for safe year-round training. Not only does the facility feature dozens of wood poles, but it also boasts a variety of industrial-grade components to create the most realistic distribution system possible.
For utility workers, real-world, hands-on training is essential. As Aguilar notes in his article:
“Because safety is an integral part of all utility work, the new training center helps the students learn through hands-on instruction. While they can pick up on key knowledge through sitting in class and reading books, the real rubber meets the road when they are actively participating in hands-on learning.”
For example, KMU’s training center allows workers “to get hands-on training in a controlled environment…[that] mitigates some of the hazards inherent in utility work, and it allows the field workers to make mistakes in a safe environment.”
KMU has found that a combination of classroom work and hands-on training is the ideal training experience. “For example, if KMU offers a workshop on transformer theory and connections, then the linemen can get hands-on experience immediately after they receive classroom instruction to connect their learning to actual work.”
Training Solutions for Everyone
 As Aguilar notes in his article, “[m]any of the members of KMU are small in scope, and as such, they don’t have the ability to provide a comprehensive training program or build a facility of their own.” That’s why the KMU training center is such an important and valuable resource for Kansas utilities.
As Aguilar notes in his article, “[m]any of the members of KMU are small in scope, and as such, they don’t have the ability to provide a comprehensive training program or build a facility of their own.” That’s why the KMU training center is such an important and valuable resource for Kansas utilities.
Nevertheless, “every utility needs to have a safe, qualified workforce.” So what are utilities in other states without the benefit of a KMU training facility supposed to do? Fortunately, there are a variety of training solutions that offer any utility the ability to provide critical hands-on skills training.
For example, DAC Worldwide manufactures a variety of unique training systems and industrial component cutaways that teach the essential hands-on skills frontline utility workers need most. In this final section, we’ll learn more about how utilities can use these systems to meet their training needs.
Transformer Wiring Training System (408-000)
 DAC Worldwide’s Transformer Wiring Training System (408-000) is a realistic training device that replicates the conditions and circumstances that a utility worker encounters when making common power transformer connections in the field. This convenient tabletop training system provides hands-on training without the danger of full-voltage field experience.
DAC Worldwide’s Transformer Wiring Training System (408-000) is a realistic training device that replicates the conditions and circumstances that a utility worker encounters when making common power transformer connections in the field. This convenient tabletop training system provides hands-on training without the danger of full-voltage field experience.
For example, a 208VAC, three-phase source is stepped down, creating a 41VAC, three-phase system. The training system includes two complete sets of three-phase transformers so that paralleling can be explored. Users will also get first-hand experience using banana jacks, ground/primary connections, and secondary connections using both three-phase and single-phase applications.
Learners will study topics like analyzing transformer single-phase/three-phase voltages, identifying transformer turns ratio (TTR), and demonstrating how connections can produce incorrect motor rotation. They will also practice hands-on skills, such as performing transformer connections, interconnecting multiple transformers in Wye or Delta configurations, and simulating a burned-out transformer in a three-phase bank.
Transformer Connections Training System (491-000)
DAC Worldwide’s Transformer Connections Training System (491-000) teaches the key skills that a utility worker must master in order to confidently operate modern generating equipment, such as the paralleling of generators and connecting to a larger power grid. The system replicates the conditions and circumstances utility workers encounter when making common transformer connections in the field.
For example, learners can practice ground connections, primary connections, and secondary connections easily using banana jacks. Both three-phase and single-phase applications are provided, and a 208 VAC, 3-phase source is stepped down to a 41 VAC, 3-phase system for safety.
Users will find that the Transformer Connections Training System provides a safe and efficient, yet realistic alternative to a full-voltage field experience. Standard accessories include patch cords, fourteen (14) transformers, a panel-mounted voltmeter and phase rotation meter.
Industrial Transformer Cutaways
 DAC Worldwide’s Single-Phase Transformer Cutaway (273-912) and Three-Phase Transformer Cutaway (273-915) are detailed, professionally-crafted transformer cutaways that depict a shell-type, single-phase transformer and a coaxially-wound, three-phase, delta-wye wired transformer, respectively.
DAC Worldwide’s Single-Phase Transformer Cutaway (273-912) and Three-Phase Transformer Cutaway (273-915) are detailed, professionally-crafted transformer cutaways that depict a shell-type, single-phase transformer and a coaxially-wound, three-phase, delta-wye wired transformer, respectively.
Through careful sectioning, the complete internal configurations of these transformers can be seen. Details shown include the laminated steel core, primary and secondary windings, and primary insulation.
Common transformer brands and models are chosen for sectioning for industrial relevance. Users will gain valuable insight into the inner workings of these transformers that they will encounter on a regular basis in the field.
- Published in News
New Marine Corps Doctrine Promotes Education & Training
Click here to view New Marine Corps Doctrine Promotes Education & Training as a multimedia presentation.
The few. The proud. Who are we talking about? The Marines, of course. That particular recruiting slogan has been permanently etched into our memories over the years.
And it’s a great slogan. The Marines are legendary for a training regimen that weeds out all but the strongest, creating a fighting force to be reckoned with. Indeed, the Marines have been on the front lines of every major U.S. military campaign of the modern era.
To be prepared for the future, however, the Marines know that training the same way they have in the past will not be sufficient. That’s why a recent doctrinal publication puts a new focus on education and continued learning.
Industry, always closely connected to the military, would do well to put a renewed emphasis on education and training, too. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how partnering with a trusted technical training company like DAC Worldwide can prepare your students, workers, soldiers, and sailors for a bright future.
A New Doctrine for a New Era
 According to a Marine Corps Times article, “the Marine Corps unveiled the Marine Corps Doctrinal Publication 7 [MCDP 7] in February [2019] as the service aims to promote education, training, and continued learning among Marines so they become students of their profession.”
According to a Marine Corps Times article, “the Marine Corps unveiled the Marine Corps Doctrinal Publication 7 [MCDP 7] in February [2019] as the service aims to promote education, training, and continued learning among Marines so they become students of their profession.”
How significant was this doctrinal development? MCDP 7 was the first new doctrinal publication issued by the Marines since 2001. Its goal: “to motivate Marines to personally assess where they can improve and understand the ‘why’ behind the significance of learning.”
Maj. Gen. William Mullen was quoted as saying “that he’s heard Marines say they joined the service to escape an academic education. But the Corps wants its personnel to understand that the two complement one another and that education prepares Marines to think quickly when faced with challenges.”
According to Mullen, “You need both training and education. Training prepares you for things you know you’re going to have to do…But the education piece comes in when the unknown starts to happen, which it always does.” Mullen specifically referred to the fact that the environments Marines face today present challenges that are only growing more complex.
This new doctrinal change comes as “Commandant of the Marine Corps Gen. David Berger is working to remake the Corps to better compete with potential high-end adversaries…Berger wants a leaner force to conduct sea denial operations, survive in a contested maritime environment and serve as a larger Naval expeditionary force.”
 It’s Not Just the Marines
It’s Not Just the Marines
Speaking of the Navy, the Marine Corps Times article notes that the Navy announced in May 2019 “that it was modifying fitness reports to reflect an individual’s educational and training accomplishments, including military education courses, professional and academic certifications, among other things.”
Like the Marines’ new focus on education and continued learning, the Navy’s modified fitness reports are meant to “show that career-long military learning isn’t only job-related technical or tactical training, and that a commitment to higher education will produce Navy leaders with more refined critical thinking skills,” according to an article in the Navy Times.
Future Navy fitness reports will thus document educational performance, including “[m]ilitary educational courses, civilian institution coursework, and professional and academic certifications.” Navy leadership also indicated they will also encourage additional informal efforts, such as learning new technologies.
 It’s All COOL
It’s All COOL
It’s no coincidence that the Marines and the Navy would emphasize professional and academic certifications. Much of the training that military personnel receive prepares them for future civilian jobs.
Obtaining professional and academic certifications while in the military can make it easier for personnel to transition to civilian life when their service is finished. All branches of the military recognize the importance of certifications in making that transition as easy as possible.
For example, the Marine Corps COOL site (Marine Corps Credentialing Opportunities On-Line) helps Marines see how their military training and experience matches up with civilian credential requirements. Such credentials could include important and valuable advanced manufacturing credentials from entities like the National Institute of Metalworking Skills (NIMS) and the Manufacturing Skill Standards Council (MSSC).
Marines using the COOL site can see whether military funding is available to help attain particular credentials. They can also see how the training and skills they’ve already acquired might match up with specific credentials valued by employers, such as NIMS’ Industrial Technology Maintenance (ITM) certification or MSSC’s Certified Production Technician (CPT) certification. There are also COOL sites for the Army, Coast Guard, Navy, and Air Force.
 Industry Must Also Evolve
Industry Must Also Evolve
Given the military’s new focus on education and continued learning, it’s important that industries that work with and support the military evolve in a similar fashion. The military-industrial complex consists of all sorts of industries that work closely with the military to help them accomplish their mission.
These industries should take a cue from their military counterparts and begin to develop a similar focus on education and continued learning among their workforce. Industry workers will only be able to continue to keep pace with their military counterparts if they’re also seeking new educational opportunities and learning new skills and technologies.
Pushing an industrial workforce or a military organization toward more education and greater skill development can be a daunting task. That’s why it’s imperative that both the military and their industrial counterparts seek out and rely upon the expertise of a trusted technical training partner.
A Trusted Education & Training Partner
DAC Worldwide is a US-based world leader in technical training solutions. For over 35 years, DAC Worldwide has been helping industrial employers and military organizations with realistic, hands-on training systems.
DAC Worldwide offers a wide range of product solutions to fit all your training needs. From training systems that teach a full range of skills to cutaways that increase understanding of how a component works, we have what you need.
For example, many military personnel work in the same skilled occupations as civilians. This means they need a solid foundation in various technologies, including electrical, electronics, fluid power, and mechanical drives.
Whether you train military personnel working on military bases or civilian crews with military contracts, DAC Worldwide’s military training solutions offer an unmatched range of products to allow you to create the course you need or to fill in any gaps that you have in your current training.
Let’s take a closer look at four specific DAC Worldwide products that can take your training program to the next level:
Lock-Out/Tag-Out Training System (811-000)
DAC Worldwide’s Lock-Out/Tag-Out Training System features a realistic, simulated working process environment that facilitates introductory training with hands-on activities related to the process of identifying and locking out sources of dangerous potential energy in an industrial setting. The training system includes two process tanks; a centrifugal pump; a complex, multi-purpose piping network; electrical controls; a variety of lockable system components; and a lock-out/tag-out kit that features a large number of commonly-encountered locking and tagging devices.
 Basic Electricity Training System (400-PAC)
Basic Electricity Training System (400-PAC)
DAC Worldwide’s Basic Electricity Training System teaches basic AC and DC electrical principles. Learners will explore how electricity is used for power and control in various sectors. The trainer covers industry-relevant skills, such as installing, operating, and troubleshooting AC and DC electrical circuits in a variety of applications.
Piston Pump Cutaway (278-132)
DAC Worldwide’s Piston Pump Cutaway is an industrial piston pump that has been carefully sectioned and color-coded to train learners in the design, operation, construction, and maintenance of this common process pump used throughout industry. The cutaway exposes and showcases the complete internal configuration of an industrial piston pump. Moreover, seal features and bearings have been retained to allow realistic, hands-on pump maintenance and operation training.
Centrifugal Pump Cutaway (278-101)
DAC Worldwide’s Centrifugal Pump Cutaway is a sectioned centrifugal pump that provides realistic training in the operating principles, construction details, and maintenance of common centrifugal process pumps used throughout industry and the military. It includes various sectioned components, such as seals and bearings, as well as showcasing the pump’s impeller.
Contact DAC Worldwide Today
Is your organization ready to take its industrial technical training to the next level? Contact a DAC Worldwide expert today for a personal consultation regarding your training needs and how our variety of training systems, cutaways, dissectibles, and models can prepare both industrial workers and military personnel for the future challenges they face.

- Published in News



















